What is a Wrist Fracture?
A wrist fracture is a break in one or more of the bones in the wrist. The wrist is made up of eight small carpal bones and the ends of the radius and ulna (the forearm bones).
Common Types of Wrist Fractures
- Distal Radius Fracture: The most common type, often occurring from a fall onto an outstretched hand.
- Scaphoid Fracture: Involves one of the small carpal bones, typically from a fall.
- Colles’ Fracture: A specific type of distal radius fracture where the broken piece of bone tilts upward.
- Smith’s Fracture: Similar to Colles’ but the broken piece tilts downward.
- Barton’s Fracture: Involves a fracture and dislocation of the wrist joint.
Symptoms of a Wrist Fracture
- Immediate pain and tenderness
- Swelling and bruising
- Visible deformity (e.g., a bent wrist)
- Difficulty moving the wrist or hand
- Numbness or tingling (if nerves are affected)
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: A doctor will check for pain, swelling, and deformity.
- X-Rays: The primary tool to confirm a fracture and assess its severity.
- CT Scan or MRI: Used in complex cases to get detailed images of bones and soft tissues.
Treatment Options
- Non-Surgical Treatment:
- Immobilization: Using a cast or splint to keep the wrist in place.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to restore movement and strength once the cast is removed.
- Surgical Treatment:
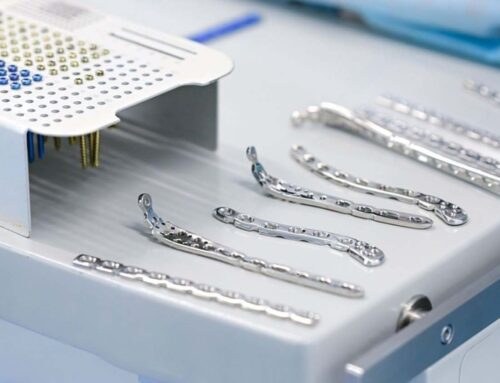
- Internal Fixation: Using metal pins, locking plates and screws to hold the bones together.
- External Fixation: Using an external fixator device to stabilize the bones during healing.
- Bone Grafting: In cases where the bone is shattered, a graft may be necessary.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Healing Time: Typically 6-8 weeks for the bone to heal, but full recovery can take several months.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy is crucial to restore full function and strength to the wrist.
- Follow-Up: Regular check-ups with the doctor to monitor healing progress.
- Preventing Wrist Fractures
- Use Protective Gear: Wrist guards during high-risk activities like skating or snowboarding.
- Improve Bone Health: Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake.
- Exercise: Strengthening exercises for the wrist and improving overall balance to prevent falls.
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- If you suspect a wrist fracture due to injury or trauma.
- If you experience severe pain, swelling, or deformity.
- If there is numbness, tingling, or difficulty moving your fingers.
Conclusion
Wrist fractures are common injuries that require prompt diagnosis and treatment to ensure proper healing and avoid complications. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment plans.





Leave A Comment