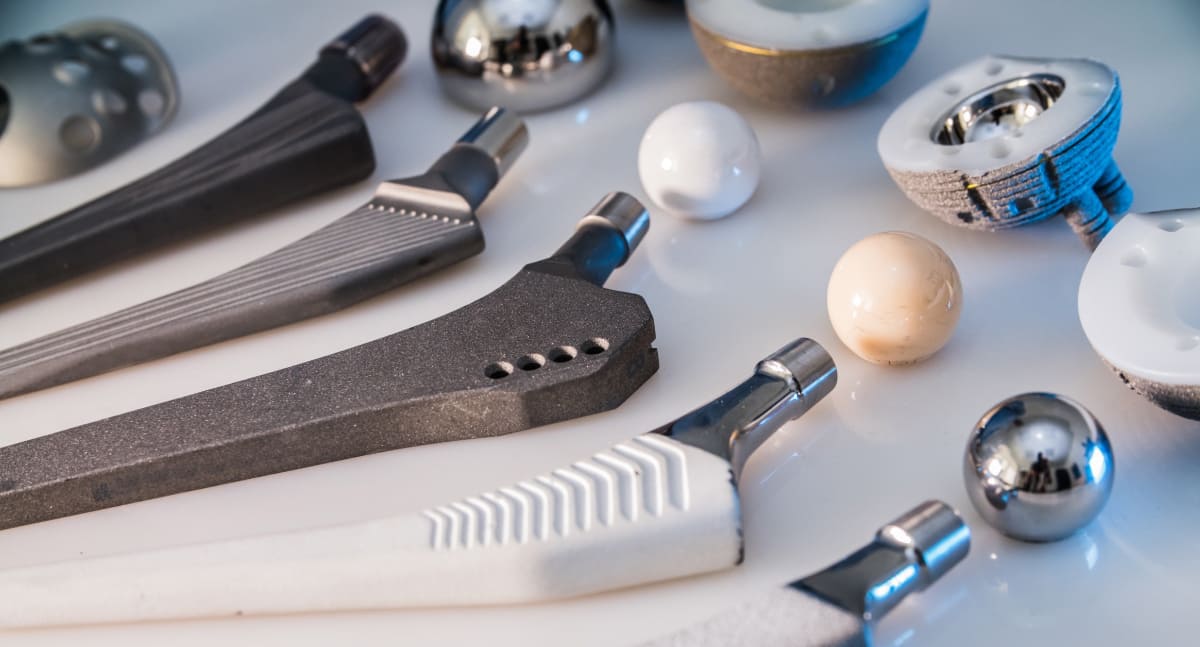
Hip implants, also known as hip prostheses or total hip replacements, are medical devices used to replace damaged or diseased hip joints. There are several types of hip implants, each designed to address different patient needs and conditions. Here are some of the most common types:
Metal-on-Polyethylene (MoP):
This type of hip implant consists of a metal femoral component that fits into the thigh bone (femur) and a plastic (polyethylene) acetabular component that replaces the hip socket.
MoP implants are widely used due to their durability and long-term clinical success. However, concerns have been raised about the potential for wear and the release of metal ions into the body.
Ceramic-on-Polyethylene (CoP):
Similar to MoP implants, CoP implants consist of a ceramic femoral component and a polyethylene acetabular component.
Ceramic implants offer excellent wear resistance and low friction properties, potentially reducing the risk of implant wear and loosening.
Metal-on-Metal (MoM):
MoM implants consist of metal components for both the femoral and acetabular parts.
While MoM implants were once popular due to their potential for reduced wear, concerns have emerged regarding metal ion release, tissue damage, and implant failure.
Ceramic-on-Ceramic (CoC):
CoC implants feature ceramic femoral and acetabular components.
These implants offer excellent wear resistance, low friction, and biocompatibility, making them a popular choice, especially for younger, more active patients.
Ceramic-on-Metal (CoM):
CoM implants combine a ceramic femoral component with a metal acetabular component.
This configuration aims to capitalize on the advantages of ceramic bearings while providing the stability and fixation offered by metal components.
Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene (HXLPE):
HXLPE is a type of polyethylene that has undergone a special manufacturing process to improve its wear resistance.
It is often used in combination with metal or ceramic femoral components to reduce wear and enhance the longevity of the implant.
Modular Implants:
Modular hip implants allow surgeons to customize the implant by selecting different combinations of femoral stems, necks, and heads to match the patient’s anatomy and specific requirements.
Resurfacing Implants:
Resurfacing implants involve capping the femoral head with a metal prosthesis rather than removing and replacing it entirely.
These implants are primarily used for younger patients with good bone quality and minimal bone loss.
Choosing the most suitable type of hip implant depends on factors such as the patient’s age, activity level, bone quality, and the surgeon’s preference and expertise. Additionally, ongoing research and advancements in materials and design continue to influence the development of hip implants in India, with the aim of improving outcomes and patient satisfaction




Leave A Comment