Locking plates are often utilized in the treatment of osteoporotic fractures due to their ability to provide stable fixation in bones with poor quality or reduced density, such as those affected by osteoporosis. Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more prone to fractures, and traditional fixation methods may not provide adequate stability.
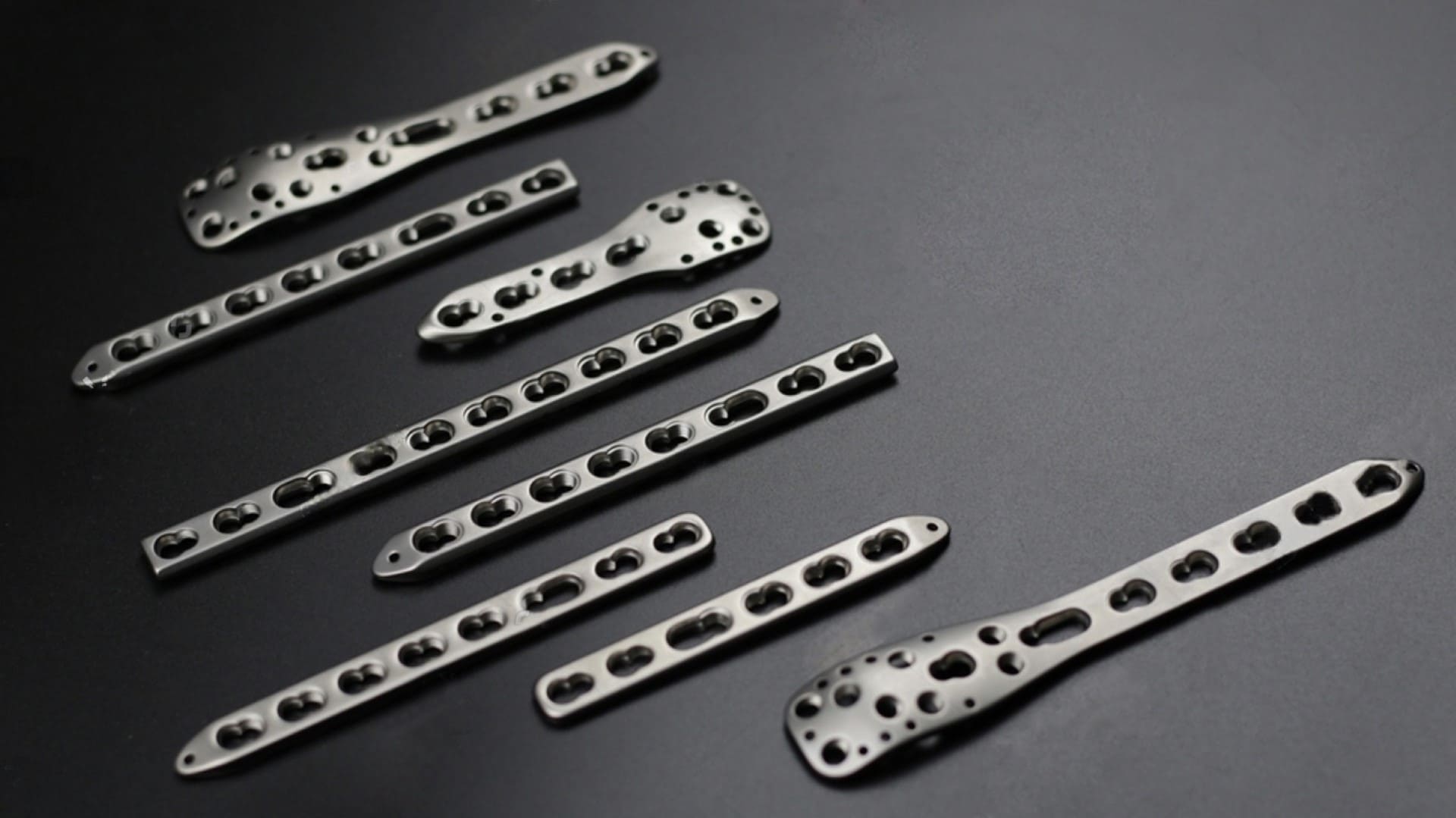
Locking plates differ from conventional plates in that they have threaded screw holes, allowing screws to lock into the plate itself, creating a fixed-angle construct. This design minimizes dependence on bone quality for screw purchase and enhances stability.
Here are some key benefits of using locking plates in the treatment of osteoporotic fractures:
Enhanced Stability:
Locking plates create a fixed-angle construct, which provides enhanced stability even in bones with reduced density.
Reduced Risk of Screw Pullout:
The locking mechanism reduces the risk of screw pullout, which is particularly beneficial in osteoporotic bone.
Improved Load Distribution:
Locking plates distribute loads more evenly across the fracture site, reducing stress on individual screws and surrounding bone.
Preservation of Fracture Hematoma:
Locking plates often allow for indirect reduction techniques, preserving the fracture hematoma, which can aid in the healing process.
Early Mobilization:
The stability provided by locking plates may allow for earlier mobilization and rehabilitation, which is crucial for overall patient recovery.
Versatility:
Locking plates come in various shapes and sizes, allowing for versatility in addressing different fracture patterns and anatomical sites.
However, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks, such as increased orthopedic implant cost and the learning curve associated with the surgical technique. Additionally, proper patient selection and surgical technique are crucial to achieving optimal outcomes when using locking plates for osteoporotic fractures.




Leave A Comment