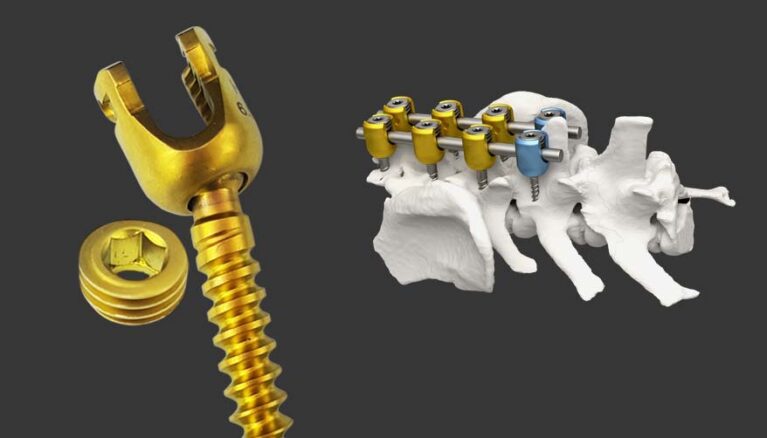
A mini polyaxial screw is a type of orthopaedic or spinal screw that allows for multi-directional movement, meaning the head of the screw can pivot in various directions before being locked into place. These screws are commonly used in:
Spinal Surgery: Particularly in procedures like cervical or thoracolumbar fixation, allowing flexibility in rod placement.
Maxillofacial Surgery: For reconstructive procedures involving the jaw or facial bones.
Small Bone Fixation: In trauma or orthopedic applications involving delicate bones, such as in the hand or foot.
Key Features of Mini Polyaxial Screws
Mini polyaxial screws are specialized implants used in spinal, orthopedic, and maxillofacial surgeries, providing flexibility and strong fixation. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their key features:
Polyaxial Head (Multidirectional Motion)
- The screw head can pivot in multiple directions (usually between 30° to 40° from the center).
- This allows surgeons to adjust the angle of the screw without having to reposition it completely.
- Enhances flexibility in placement, especially in complex anatomical structures like the spine, jaw, or small bones in extremities.
Locking Mechanism
- Once the screw is positioned correctly, a locking mechanism (such as a set screw or locking cap) is used to secure it in place.
- This prevents unwanted movement, ensuring stable fixation post-surgery.
- Often used in spinal rod constructs to create a rigid fixation for spinal stabilization.
Material Composition (Biocompatible and Durable)
- Usually made from Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) or Stainless Steel, both known for their biocompatibility, strength, and corrosion resistance.
- Some screws are coated with hydroxyapatite to enhance bone integration.
Thread Design (Enhanced Bone Grip)
- The screw threads are designed to provide strong anchorage in cortical and cancellous bone.
- Some mini polyaxial screws have dual-threaded designs for better grip in both soft and hard bone.
- Self-tapping or self-drilling options are available for easy insertion without pre-drilling.
Miniature Size for Delicate Structures
Mini polyaxial screws are smaller than standard polyaxial screws, making them ideal for:
- Cervical spine fixation
- Facial and mandibular reconstruction
- Small bone trauma repair (hand, foot, wrist)
Compatibility with Rods and Plates
- Designed to work with mini rods, plates, or interconnecting components used in spinal or maxillofacial surgeries.
- The polyaxial motion helps align the screw with the rod without excessive force.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Applications
- These screws are often used in percutaneous (minimally invasive) techniques, reducing surgical trauma and recovery time.
- Can be inserted using cannulated (hollow) designs that allow for precise placement using guidewires.
Radiolucency and Imaging Compatibility
- Titanium screws are MRI and CT-compatible, producing minimal artifacts in medical imaging.
- Some screws have markings or coatings to enhance X-ray visibility.
Applications of Mini Polyaxial Screws
- Spinal fixation (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions)
- Maxillofacial reconstruction (jaw fractures, mandibular plating)
- Small bone fixation (hands, feet, and wrists)
- Trauma surgery and fracture management
Benefits of Mini Polyaxial Screws
Mini polyaxial screws offer several advantages in spinal, orthopedic, and maxillofacial surgeries. Their small size and polyaxial movement make them ideal for delicate anatomical structures while ensuring strong fixation and stability.
Greater Flexibility in Screw Placement
- The polyaxial head allows multidirectional movement (typically 30°–40°), making it easier for surgeons to position the screw at the optimal angle.
- Useful in complex anatomical areas such as the cervical spine, facial bones, or small extremities where precise angulation is critical.
Improved Surgical Accuracy and Stability
- Provides secure fixation with a locking mechanism that prevents unwanted movement after placement.
- Reduces the need for excessive repositioning, minimizing surgical trauma.
- Allows for strong anchoring in both cortical and cancellous bone.
Enhanced Biomechanical Strength
- Mini polyaxial screws distribute forces more evenly, reducing stress concentrations that can lead to implant failure.
- The thread design ensures firm grip in small or fragile bones, minimizing the risk of loosening over time.
Compatibility with Rods, Plates, and Other Implants
- Easily integrates with mini-rod systems, plates, and connectors, making them versatile for different fixation techniques.
- The ability to adjust the screw angle before final locking simplifies the placement of rods or plates
Ideal for Minimally Invasive Procedures
Mini polyaxial screws are small in size, allowing for less invasive surgical techniques.
Reduces soft tissue damage, leading to:
- Faster recovery time
- Less post-operative pain
- Reduced risk of infection
Strong Biocompatibility & Corrosion Resistance
Usually made from Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) or Stainless Steel, ensuring:
- Excellent biocompatibility (minimizing allergic reactions or rejection)
- Corrosion resistance (for long-term durability inside the body)
- MRI & CT compatibility (for clear post-operative imaging)
Secure Fixation in Small & Fragile Bones
- Their miniature size makes them perfect for small bones in the hand, foot, jaw, and cervical spine, where traditional screws may be too large.
- Prevents bone fractures or stress concentration, ensuring long-term stability.
Lower Risk of Implant Failure
The locking mechanism and strong thread grip reduce the chances of:
- Screw loosening
- Rod or plate misalignment
- Reoperation due to implant failure
Versatility Across Multiple Surgical Specialties
- Used in spinal fixation, trauma surgery, maxillofacial reconstruction, and small bone repairs.
- Suitable for treating fractures, degenerative diseases, deformities, and reconstructive procedures.
Role of Mini Polyaxial Screws in Orthopaedic Implants
Mini polyaxial screws play a crucial role in orthopaedic implants by providing secure fixation with adjustable angulation, making them ideal for small bone fractures, spinal stabilization, and maxillofacial reconstruction.
Key Functions:
- Spinal Fixation – Used in cervical and thoracolumbar fusion to stabilize the spine and connect rods.
- Small Bone Repair – Ideal for hand, foot, and wrist fractures, ensuring precise fixation.
- Maxillofacial Surgery – Used in jaw reconstruction and facial trauma for stable bone alignment.
- Trauma and Deformity Correction – Helps correct bone deformities and fractures with flexible positioning.
These screws enhance surgical precision, biomechanical strength, and post-operative recovery, making them a key component in modern orthopaedic implants.
Conclusion
Mini polyaxial screws are highly versatile, biomechanically strong, and minimally invasive, making them a preferred choice for delicate surgical applications. Their ability to provide secure fixation while allowing for flexible placement enhances surgical outcomes and patient recovery.



Leave A Comment