Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or worn-out hip joint with an artificial joint, called a prosthesis, to relieve pain and improve function. This procedure is commonly performed to treat severe arthritis or hip fractures that have not responded to other treatments.
Here’s an overview of the process:
Preparation:
Before the surgery, the patient will undergo a series of pre-operative evaluations, including physical exams, blood tests, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. The patient may also need to adjust their medications or stop certain medications prior to surgery.
Anesthesia:
During the surgery, the patient is given anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and pain-free. The type of anesthesia used may vary depending on the patient’s health and the surgeon’s preference. Options include general anesthesia, regional anesthesia (spinal or epidural), or a combination of both.
Surgical Procedure:
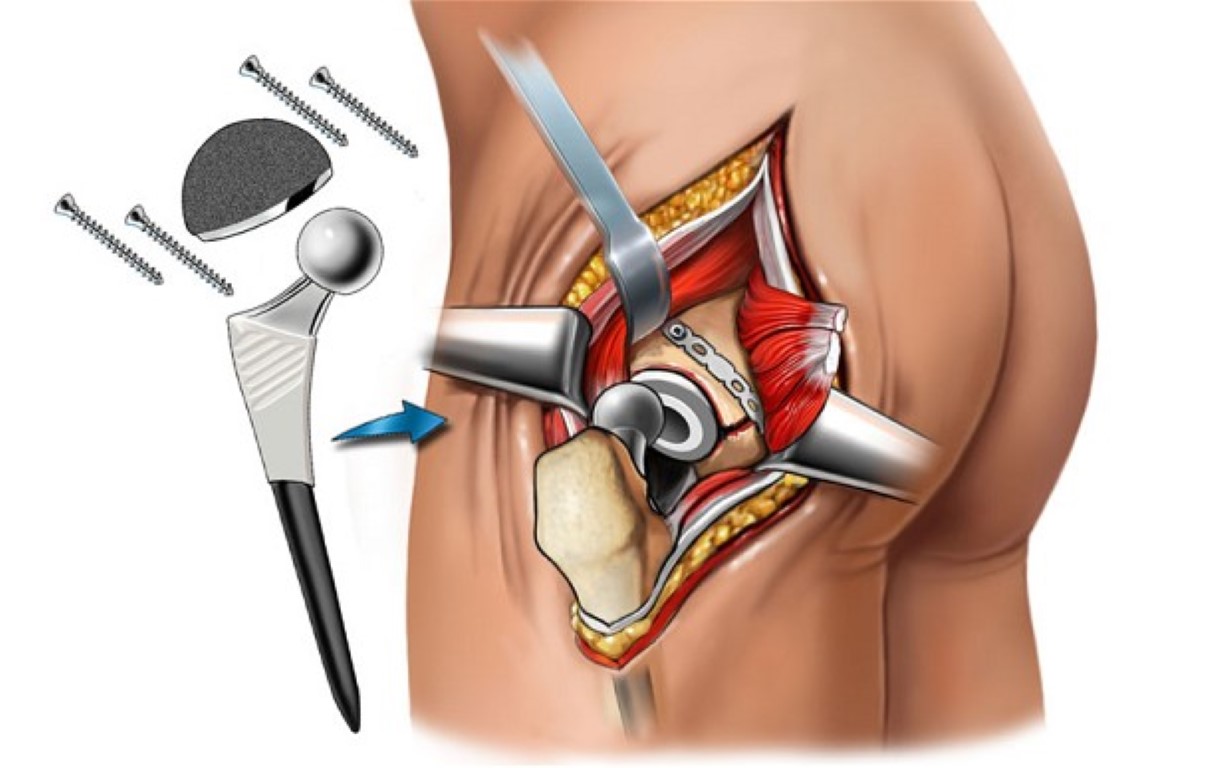
The surgeon makes an incision over the hip joint, usually on the side or front of the hip.
The damaged bone and cartilage are removed from the hip joint.
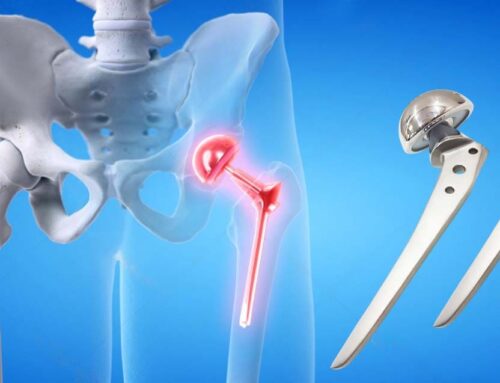
The artificial joint components, typically made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials, are implanted into the hip socket (acetabulum) and the femur (thigh bone).
The artificial components may be cemented into place or may be designed for bone to grow into them for stability.
Recovery:
After the surgery, the patient is monitored in a recovery area until they wake up from anesthesia.
Physical therapy usually begins soon after surgery to help regain strength and mobility in the hip joint.
The length of hospital stay varies, but most patients can expect to stay in the hospital for a few days.
Patients may need assistive devices such as crutches or a walker initially and then transition to using a cane as they recover.
Full recovery can take several weeks to months, during which time patients gradually increase their activity levels and continue with physical therapy exercises.
Post-operative Care:
Patients will be given instructions for wound care, pain management, and activity restrictions.
Follow-up appointments with the surgeon are necessary to monitor healing and progress.
It’s important for patients to adhere to any precautions or restrictions provided by their surgeon to prevent complications and promote successful outcomes.
Hip replacement surgery is generally considered safe and effective for relieving pain and improving mobility in patients with severe hip joint damage. However, as with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications, including infection, blood clots, dislocation of the artificial joint, and nerve or blood vessel injury. It’s essential for patients to discuss these risks with their healthcare team and carefully follow their pre- and post-operative instructions for the best possible outcome.


Leave A Comment